A lecture with the topic of “A Study on the Sustainability of Tourist Destinations from the Sharing Economy and Crowd-sourcing” was successfully held by the Department of Tourism Management from 10:30 to 12:00 on December 17th, 2022. This academic lecture has invited Prof. Billy Bai, a doctoral supervisor and the Associate Dean of College of Hotel Administration from the University of Nevada Las Vegas (UNLV). Several faculties including Liu Peisong, Zhou Lingxu and Zhou Lili as well as around forty postgraduates and undergraduates from the Department of Tourism Management attended this lecture, which was presided over by the associate professor Li Minglong.

As an internationally known expert in hospitality and tourism marketing, Prof. Bai has almost 80 articles published in top-tier journals, which have frequently been cited. He also won numerous awards, including the best paper awards from the Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research (JHTR) and the annual I-CHRIE (International Council on Hotel, Restaurant, and Institutional Education) conference. Besides, Prof. Bai has been listed in Who’s Who in America in 2010.
Based on his latest study results, Prof. Bai addressed this lecture on the theme of “A Study on the Sustainability of Tourist Destinations from the Sharing Economy and Crowd-sourcing”. After sharing two researches on how to achieve the sustainability of tourist destinations based on the sharing economy and crowd-sourcing, he put forward corresponding proposals to achieve the sustainability of tourist destinations in a more comprehensive and thorough way.
The sharing economy is key to study one. According to Prof. Bai, the sharing economy rockets up exponentially in recent years, which has become a potential avenue for the sustainability of tourist destinations. However, the concept of or approaches to systematically evaluating the sustainability and effects of the sharing economy have not been proposed, which forms a blank area of relevant researches. Therefore, this is a study with the goal of establishing a comprehensive conceptual framework of sustainability so as to prove how the sharing economy strengthens the sustainability of tourist destinations.
Up next, Prof. Bai measured the sustainability of tourist destinations on the basis of the capital theory approach. Specifically, he explored four capitals of tourist destinations (human capital, natural capital, man-made capital and social capital) through integrating three theories (stakeholder theory, resource theory and service-dominant logic). Based on the stakeholder theory, he proposed that human capital is equivalent to the competence of five stakeholders combined, including the government, tourists, local community, travel agencies and non-travel firms. Resource theory argues that resources constitute the natural and man-made capital of tourist destinations, in which resources owned by all entities are a prerequisite for exchanges. Specifically, the resources of travelers are time, money and participation; the local residents’ resources are real ones; the resources of a sharing economic platform are online platforms; the government’s resources are the law and public resources; the resources of travel agencies are periodicity and authenticity. The service-dominant logic believes that services and exchanges of stakeholders could provide a systematic perspective on achieving values, and all the stakeholders could create values of services through services and exchanges.
In study two, Prof. Bai further explored the sustainable development of tourist destinations guided by the concept of crowd-sourcing. Crowd-souring can attract/bring out the crowd or open population to participate in commercial activities in order to solve problems, finish tasks, come up with new ideas and produce services. Besides, the participators can conveniently utilize their dispersed money via web supported by information technology. Hence crowd-sourcing has an advantage in cost savings, speed, quality, flexibility and diversity.
The present academic studies in tourism mainly use crowd-sourcing as the source of data production instead of exploring its potential operating mechanism in practice, which lack studies in crowd-sourcing mechanism of travel applications. This means that the academia has not researched into the basic principles and frameworks of crowd-souring. Therefore, this study aims at building a crowd-sourcing framework to reveal the basic mechanism and structure of the tourism industry.
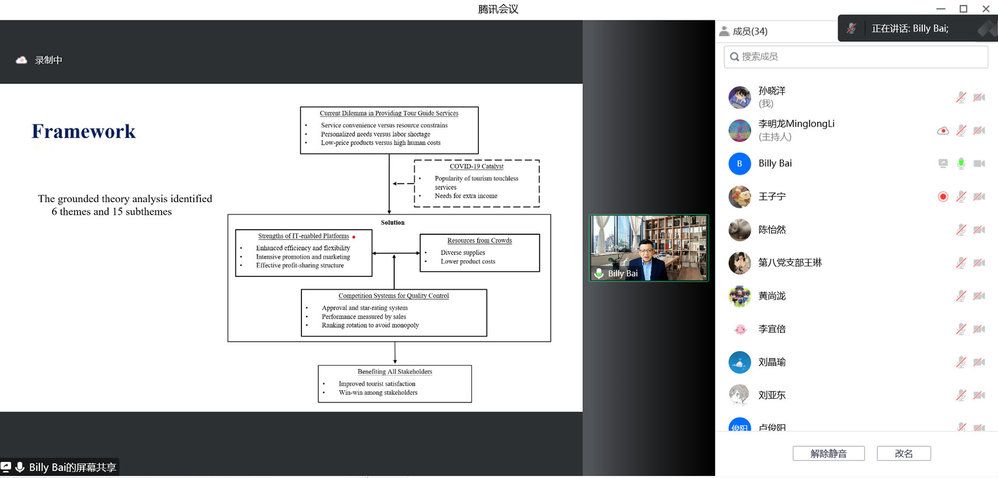
The present travel services are mainly facing three problems: service convenience and resource constraints, individual demands and labor shortages, low prices and high human costs. Correspondingly, Prof. Bai proposed a problem-solving framework based on crowd-sourcing and sharing economy, and several suggestions to achieve the sustainability of tourist destinations in a more comprehensive and thorough way. This study adopts the grounded theory as its research method. As a classical qualitative research method, this method aims to find new theories through qualitative data. Through further interviews with stakeholders, this study delved deeply into conditions, processes and results of the application of crowd-sourcing into tourism industry to build a crowd-sourcing framework and then reveal the basic mechanism and structure of tourism industry.
In addition, Prof. Bai gave detailed answers to questions asked by faculties and learners, including the application and notes of the grounded theory, the writing of academic papers as well as the publication of journal papers.
Finally, the associate professor Li Minglong summarized this lecture. The participants all said this lecture was extraordinarily inspiring and expressed their gratitude to Prof. Bai. And this lecture ended satisfactorily.
